# Controlo de Fluxo
# Instruções IF-ELSE e SWITCH
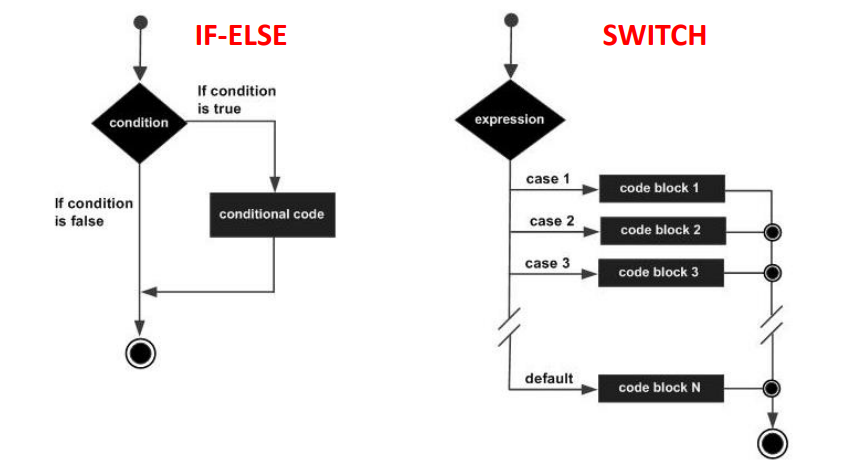
As instruções IF-ELSE e SWITCH permitem avaliar condições e desse modo condicionar o fluxo do programa.
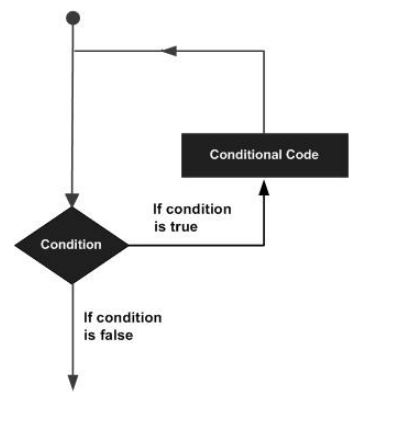
# Instrução IF
An if statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements.
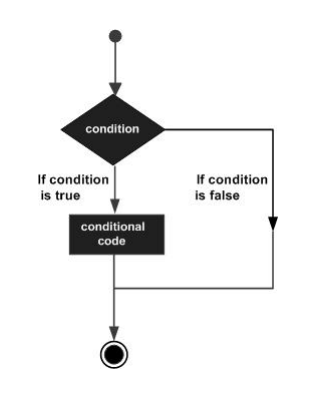
if(boolean_expression) {
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true*/
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
/* local variable definition */
int a = 10;
/* check the boolean condition using if statement */
if( a < 20 ) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
printf("a is less than 20\n");
}
printf("value of a is : %d\n", a);
return 0;
}
# Instrução IF-ELSE
An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the Boolean expression is false.
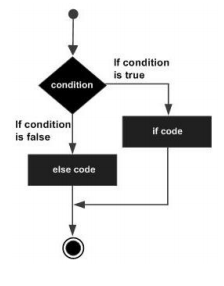
if(boolean_expression) {
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true*/
} else {
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is false*/
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
/* local variable definition */
int a = 100;
/* check the boolean condition using if statement */
if( a < 20 ) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
printf("a is less than 20\n");
} else {
/* if condition is false then print the following */
printf("a is not less than 20\n");
}
printf("value of a is : %d\n", a);
return 0;
}
# Instrução IF-ELSE encadeado
You can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement(s).
if(boolean_expression 1) {
/* Executes when the boolean expression 1 is true */
} else if( boolean_expression 2) {
/* Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true */
} else if( boolean_expression 3) {
/* Executes when the boolean expression 3 is true */
} else {
/* executes whem none of the conditions above is true */
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
/* local variable definition */
int a = 100;
/* check the boolean condition using if statement */
if( a == 10 ) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
printf("Value of a us 10\n");
} else if( a == 20) {
/* if else if condition is true */
printf("Value of a is 20\n");
} else if (a == 30) {
/* if else if condition is true */
printf("None of the values is matching\n" );
} else {
/*if none of the conditions is true*/
printf("None of the values is matching" );
}
printf("Exact value of a is : %d\n", a);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
// local variable definition
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
//check the boolean condition
if( a == 100 ){
//if confidition is true then check the following
if( b==200 ){
//if condition is true then print the following
printf("Value of a is 100 and b is 200\n");
}
}
printf("Exact value of a is : %d\n", a );
printf("Exact value of b is : %d\n", b);
return 0;
}

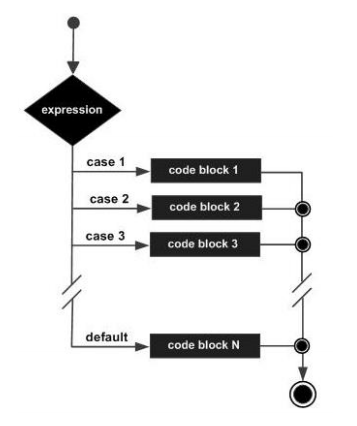
# Instrução SWITCH
A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values.
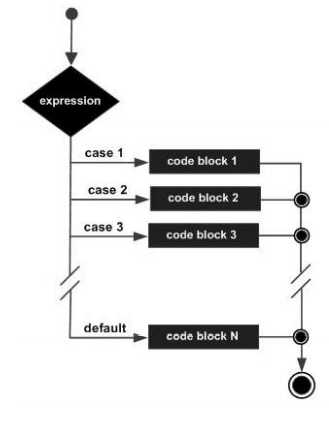
switch(expression){
case constant-expression :
statement(s);
break; /* optional */
case constant-expression :
statement(s);
break; /* optional */
/* you can have any number of case statements */
default : /* optional */
statement(s);
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
/* local variable definition */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
switch(a) {
case 100:
printf("This is part of outer switch\n", a );
switch(b) {
case 200:
printf("This is part of inner switch\n", a );
}
}
printf("Exact value of a is : %d\n", a );
printf("Exact value of b is : %d\n", b );
return 0;
}

# Ciclos: WHILE, FOR e DO WHILE
As instruções WHILE, FOR e DO WHILE permitem implementar ciclos e, desse modo, repetir a execução de um bloco de código enquanto se verifique uma determinada condição.
# Introdução WHILE
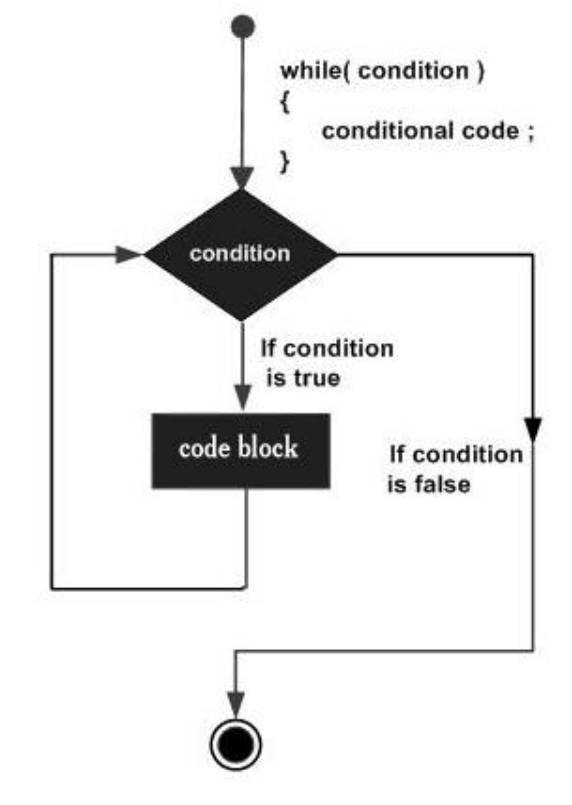
Repeats a statement or group of statements while a given condition is true. It tests the condition before executing the loop body.
while(condition) {
statement(s);
}
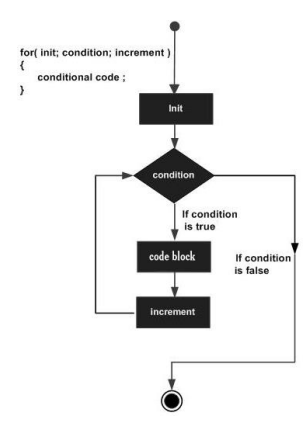
# Instrução FOR
for ( init; condition; increment ) {
statement(s);
}
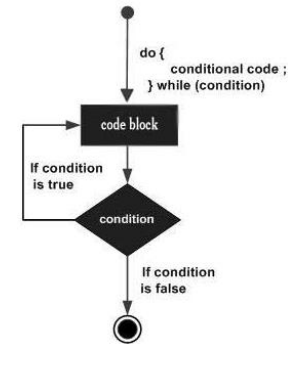
# Instrução DO … WHILE
It is more like a while statement, except that it tests the condition at the end of the loop body.
do{
statement(s);
} while( condition );
# Ciclos Encadeados
You can use one or more loops inside any other while, for, or do... while loop.
for ( init; condition; increment ) {
for( init; condition; increment ) {
statement(s);
}
statement(s);
}
while(condition) {
while(condition) {
statement(s);
}
statement(s);
}
do {
statement(s);
do{
statement(s);
}while( condition );
}while( condition );
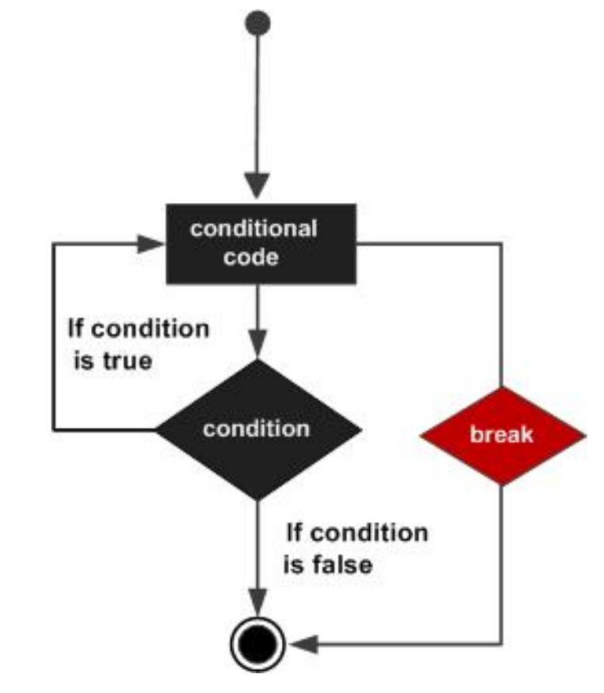
# Instrução BREAK
Terminates the loop or switch statement and transfers execution to the statement immediately following the loop or switch.
A instrução BREAK termina o ciclo ou o SWITCH que esteja a executar.